Cuts of Meat - Carving for Turkey, Chicken, Pheasant, Pigeon, Lamb, Beef, Venison
Carving meat correctly, and knowing how to cook the various meat cuts can make the difference between eating a wonderful piece of meat, or chewing something that resembles your shoe leather. Learn all about the various cuts of meat of the animal and the best methods of carving.
A word about the care of carving knives: a fine steel knife should not come in contact with intense heat, because it destroys its sharp edge. Table carving knives should not be used in the kitchen, either around the stove, or for cutting bread, meats, vegetables, etc.; a fine whetstone should be kept for sharpening, and the knife cleaned carefully to avoid dulling its edge, all of which is quite essential to successful carving of cuts of meat.
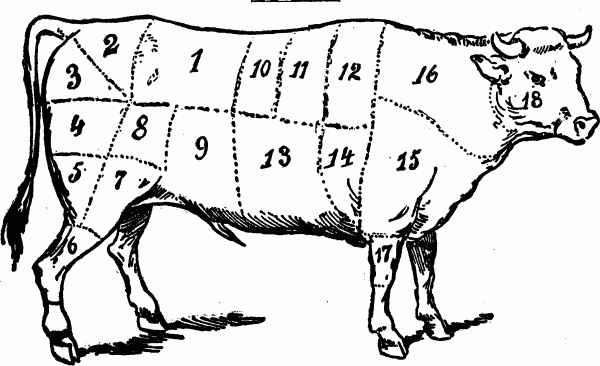
CUTS OF MEAT for BEEF HIND-QUARTER
No. 1. Loin, used for choice roasts, the porterhouse and sirloin steaks.
No. 2. Rump, used for steaks, stews and corned beef.
No. 3. Aitch-bone, used for boiling-pieces, stews and pot roasts.
No. 4. Buttock or round, used for steaks, pot roasts, beef a la mode; also a prime boiling-piece.
No. 5. Mouse-round, used for boiling and stewing.
No. 6. Shin or leg, used for soups, hashes, etc.
No. 7. Thick flank, cut with under fat, is a prime boiling-piece, good for stews and corned beef, pressed beef.
No. 8. Veiny piece, used for corned beef, dried beef.
No. 9. Thin flank, used for corned beef and boiling-pieces.
CUTS OF MEAT FOR BEEF FORE-QUARTER
No. 10. Five ribs called the fore-rib. This is considered the primest piece for roasting; also makes the finest steaks.
No. 11. Four ribs, called the middle ribs, used for roasting.No. 12. Chuck ribs, used for second quality of roasts and steaks.
No. 13. Brisket, used for corned beef, stews, soups and spiced beef.
No. 14. Shoulder-piece, used for stews, soups, pot-roasts, mince-meat and hashes.
Nos. 15, 16. Neck, clod or sticking-piece used for stocks, gravies, soups, mince-pie meat, hashes, bologna sausages, etc.
No. 17. Shin or shank, which is cut from either the leg or the shoulder as a lot of muscle and so therefore used mostly for soups and stewing.
No. 18. Cheek.
The following is a classification of the qualities of cuts of meat, according to the several joints of beef, when cut up.First Class — Cuts of meat include the sirloin with the kidney suet (1), the rump steak piece (2), the fore-rib (11).
Second Class — Cuts of meat include the buttock or round (4), the thick flank (7), the middle ribs (11).
Third Class — Cuts of meat include the aitch-bone (3), the mouse-round (5), the thin flank (8, 9), the chuck (12), the shoulder-piece (14), the brisket (13).
Fourth Class — Cuts of meat include the clod, neck and sticking-piece (15, 16).
Fifth Class — Cuts of meat include the shin or shank (17).
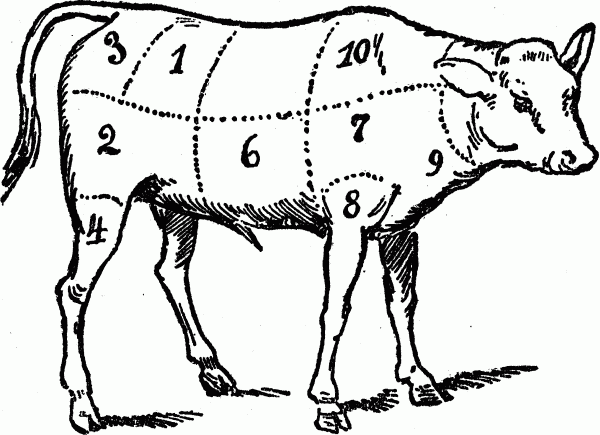
How to Cook the Different Parts of a Veal Hind Quarter
CUTS OF MEAT FOR VEAL HIND-QUARTER
No. 1. Cuts of meat include the loin, the choicest cuts used for roasts and chops.No. 2. Cuts of meat include the fillet, used for roasts and cutlets.
No. 3. Cuts of meat include the loin, chump-end used for roasts and chops.
No. 4. Cuts of meat include the hind-knuckle or hock, used for stews, pot-pies, meat-pies.
CUTS OF MEAT FOR VEAL FORE-QUARTER
No. 5. Cuts of meat include the neck, best end used for roasts, stews and chops.
No. 6. Cuts of meat include the breast, best end used for roasting, stews and chops.
No. 7. Cuts of meat include the blade-bone, used for pot-roasts and baked dishes.
No. 8. Cuts of meat include the fore-knuckle, used for soups and stews.
No. 9. Cuts of meat include the breast, brisket-end used for baking, stews and pot-pies.
No. 10. Cuts of meat include the neck, scrag-end used for stews, broth, meat-pies, etc.
In cutting up veal, generally, the hind-quarter is divided into loin and leg, and the fore-quarter into breast, neck and shoulder.
The Several Parts of a Moderately-sized, Well-fed Calf, about eight weeks old, are nearly of the following weights:—Loin and chump, 18 lbs.; fillet, 12 lbs.; hind-knuckle, 5 lbs.; shoulder, 11 lbs.; neck, 11 lbs.; breast, 9 lbs., and fore-knuckle, 5 lbs.; making a total of 144 lbs. weight.
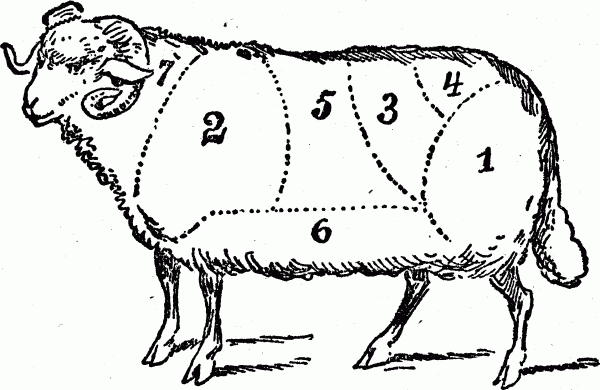
CUTS OF MEAT FOR MUTTON
No. 1. Cuts of meat include the leg, used for roasts and for boiling.
No. 2. Cuts of meat include the shoulder, used for baked dishes and roasts.
No. 3. Cuts of meat include the loin, best end used for roasts, chops.
No. 4. Cuts of meat include the loin, chump-end used for roasts and chops.
No. 5. Cuts of meat include the rack, or rib chops, used for French chops, rib chops, either for frying or broiling; also used for choice stews.
No. 6. Cuts of meat include the breast, used for roast, baked dishes, stews, chops.
No. 7. Cuts of meat include neck or scrag-end, used for cutlets, stews and meat-pies.
NOTE.—A saddle of mutton or double loin is two loins cut off before the carcass is split open down the back. French chops are a small rib chop, the end of the bone trimmed off and the meat and fat cut away from the thin end, leaving the round piece of meat attached to the larger end, which leaves the small rib-bone bare. Very tender and sweet.
Mutton is prime when cut from a carcass which has been fed out of doors, and allowed to run upon the hillside; they are best when about three years old. The fat will then be abundant, white and hard, the flesh juicy and firm, and of a clear red color.
For mutton roasts, choose the shoulder, the saddle, or the loin or haunch. The leg should be boiled. Almost any part will do for broth.
Lamb born in the middle of the winter, reared under shelter, and fed in a great measure upon milk, then killed in the spring, is considered a great delicacy, though lamb is good at a year old. Like all young animals, lamb ought to be thoroughly cooked, or it is most unwholesome.
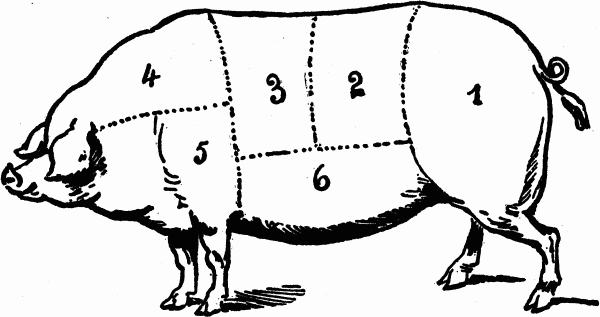
How to Cook the Different Parts of a Whole Pig
CUTS OF MEAT FOR PORK
No. 1. Leg, used for smoked hams, roasts and corned pork.
No. 2. Hind-loin, used for roasts, chops and baked dishes.
No. 3. Fore-loin or ribs, used for roasts, baked dishes or chops.
No. 4. Spare-rib, used for roasts, chops, stews.
No. 5. Shoulder, used for smoked shoulder, roasts and corned pork.
No. 6. Brisket and flank, used for pickling in salt and smoked bacon.
The cheek is used for pickling in salt, also the shank or shin. The feet are usually used for souse and jelly.
For family-use the leg is the most economical, that is when fresh, and the loin the richest. The best pork is from carcasses weighing from fifty to about one hundred and twenty-five pounds. Pork is a white and close meat, and it is almost impossible to over-roast or cook it too much; when underdone it is exceedingly dangerous and you could end up with tape worm.
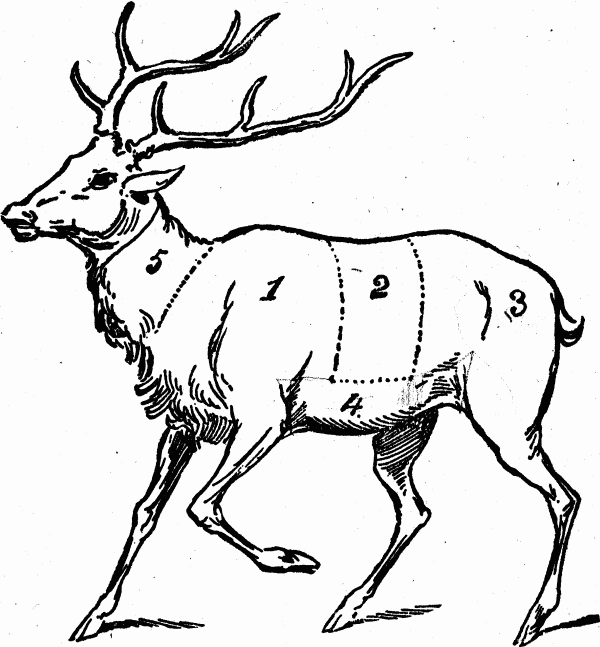
CUTS OF MEAT FOR VENISON
No. 1. Cuts of meat include the shoulder, used for roasting; it may be boned and stuffed, then afterwards baked or roasted.
No. 2. Cuts of meat include the fore-loin, used for roasts and steaks.
No. 3. Cuts of meat include the haunch or loin, used for roasts, steaks, stews. The ribs cut close may be used for soups. Good for pickling and making into smoked venison.
No. 4. Cuts of meat include the breast, used for baking dishes, stewing.
No. 5. Cuts of meat include the scrag or neck, used for soups.
The choice of venison should be judged by the fat, which, when the venison is young, should be thick, clear and close, and the meat a very dark red. The flesh of a female deer about four years old, is the sweetest and best of venison.Buck venison, which is in season from June to the end of September, is finer than doe venison, which is in season from October to December. Neither should be dressed at any other time of year, and no meat requires so much care as venison in killing, preserving and dressing.
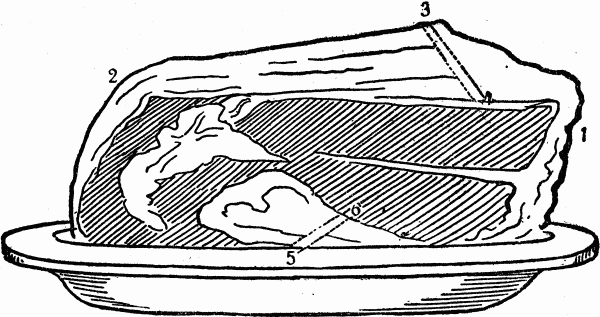
HOW TO CARVE A SIRLOIN ROAST BEEF
This choice roasting-piece should be cut with one good firm stroke from end to end of the joint, at the upper part, in thin, long, even slices in the direction of the line from 1 to 2, cutting across the grain, serving each guest with some of the fat with the lean; this may be done by cutting a small, thin slice from underneath the bone from 5 to 6, through the tenderloin.Another way of carving this piece, and which will be of great assistance in doing it well, is to insert the knife just above the bone at the bottom, and run sharply along, dividing the meat from the bone at the bottom and end, thus leaving it perfectly flat; then carve in long, thin slices the usual way. When the bone has been removed and the sirloin rolled before it is cooked, it is laid upon the platter on one end, and an even, thin slice is carved across the grain of the upper surface.
Roast ribs should be carved in thin, even slices from the thick end towards the thin in the same manner as the sirloin; this can be more easily and cleanly done if the carving knife is first run along between the meat and the end and rib-bones, thus leaving it free from bone to be cut into slices.
Tongue.—To carve this it should be cut crosswise, the middle being the best; cut in very thin slices, thereby improving its delicacy, making it more tempting; as is the case of all well-carved meats. The root of the tongue is usually left on the platter.
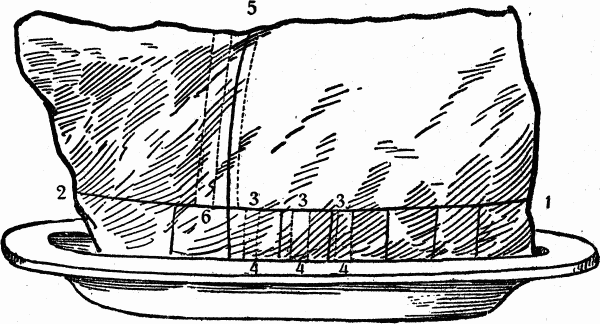
HOW TO CARVE BREAST OF VEAL
This piece is quite similar to a fore-quarter of lamb after the shoulder has been taken off. A breast of veal consists of two parts, the rib-bones and the gristly brisket. These parts may be separated by sharply passing the carving knife in the direction of the line from 1 to 2; and when they are entirely divided, the rib-bones should be carved in the direction of the line from 5 to 6, and the brisket can be helped by cutting slices from 3 to 4.The carver should ask the guests whether they have a preference for the brisket or ribs; and if there be a sweetbread served with the dish, as is frequently with this roast of veal, each person should receive a piece.
Though veal and lamb contain less nutrition than beef and mutton, in proportion to their weight, they are often preferred to these latter meats on account of their delicacy of texture and flavor. A whole breast of veal weighs from nine to twelve pounds.

CARVING A FILLET OF VEAL
A fillet of veal is one of the prime roasts of veal; it is taken from the leg above the knuckle; a piece weighing from ten to twelve pounds is a good size and requires about four hours for roasting. Before roasting, it is dressed with a force meat or stuffing placed in the cavity from where the bone was taken out and the flap tightly secured together with skewers; many bind it together with tape.
To carve it, cut in even thin slices off from the whole of the upper part or top, in the same manner as from a rolled roast of beef, as in the direction of the figs. 1 and 2; this gives the person served some of the dressing with each slice of meat.
Veal is very unwholesome unless it is cooked thoroughly, and when roasted should be of a rich brown color. Bacon, fried pork, sausage-balls, with greens, are among the accompaniments of roasted veal, also a cut lemon.
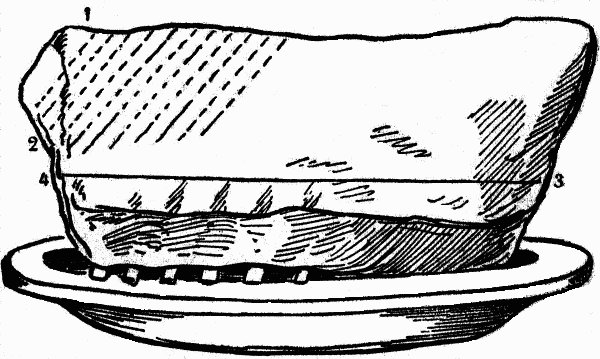
CARVING A NECK OF VEAL
The best end of a neck of veal makes a very good roasting-piece; it, however, is composed of bone and ribs that make it quite difficult to carve, unless it is done properly.To attempt to carve each chop and serve it, you would not only place too large a piece upon the plate of the person you intend to serve, but you would waste much time, and should the vertebrate have not been removed by the butcher, you would be compelled to exercise such a degree of strength that would make one's appearance very ungraceful, and possibly, too, throwing gravy over your neighbor sitting next to you.
The correct way to carve this roast is to cut diagonally from fig. 1 to 2, and help in slices of moderate thickness; then it may be cut from 3 to 4, in order to separate the small bones; divide and serve them, having first inquired if they are desired.
This joint is usually sent to the table accompanied by bacon, ham, tongue, or pickled pork, on a separate dish and with a cut lemon on a plate. There are also a number of sauces that are suitable with this roast.
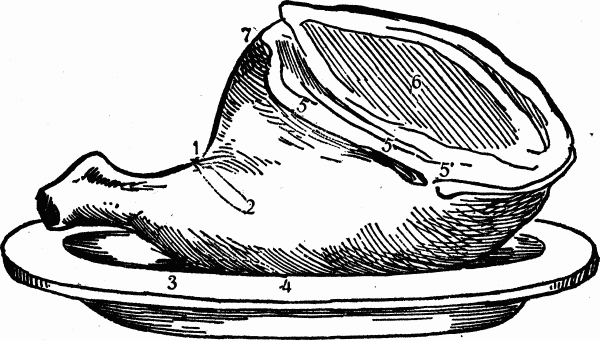
HOW TO CARVE A LEG OF LAMB or LEG OF MUTTON
In carving a roasted leg, the best slices are found by cutting quite down to the bone, in the direction from 1 to 2, and slices may be taken from either side.
Some very good cuts are taken from the broad end from 5 to 6, and the fat on this ridge is very much liked by many. The cramp-bone is a delicacy, and is obtained by cutting down to the bone at 4, and running the knife under it in a semicircular direction to 3. The nearer the knuckle the drier the meat, but the under side contains the most finely grained meat, from which slices may be cut lengthwise. When sent to the table a frill of paper around the knuckle will improve its appearance.
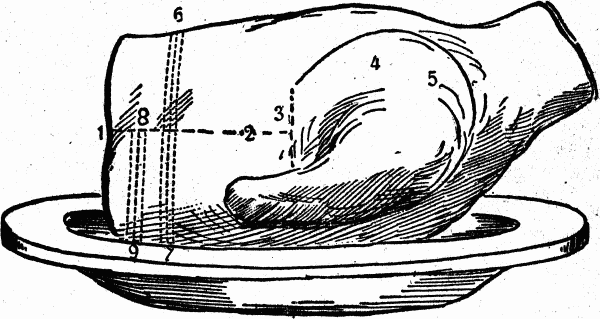
HOW TO CARVE A FORE-QUARTER OF LAMB
The first cut to be made in carving a fore-quarter of lamb is to separate the shoulder from the breast and ribs; this is done by passing a sharp carving knife lightly around the dotted line as shown by the figs. 3, 4 and 5, so as to cut through the skin, and then, by raising with a little force the shoulder, into which the fork should be firmly fixed, it will easily separate with just a little more cutting with the knife; care should be taken not to cut away too much of the meat from the breast when dividing the shoulder from it, as that would mar its appearance. The shoulder may be placed upon a separate dish for convenience.The next process is to divide the ribs from the brisket by cutting through the meat in the line from 1 to 2; then the ribs may be carved in the direction of the line 6 to 7, and the brisket from 8 to 9. The carver should always ascertain whether the guest prefers ribs, brisket, or a piece of the shoulder.
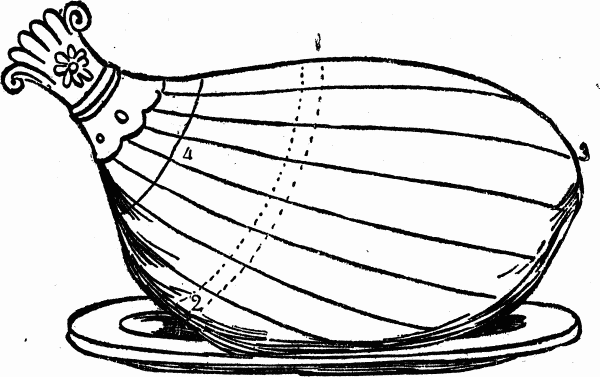
HOW TO CARVE A HAM
The carver in cutting a ham must be guided according as he desires to practice economy, or have at once fine slices out of the prime part. Under the first supposition, he will commence at the knuckle end, and cut off thin slices toward the thick and upper part of the ham.To reach the choicer portion of the ham, the knife, which must be very sharp and thin, should be carried quite down to the bone through the thick fat in the direction of the line from 1 to 2.
The slices should be even and thin, cutting both lean and fat together, always cutting down to the bone. Some cut a circular hole in the middle of a ham gradually enlarging it outwardly. Then again many carve a ham by first cutting from 1 to 2, then across the other way from 3 to 4.
Remove the skin after the ham is cooked and send to the table with dots of dry pepper or dry mustard on the top, a tuft of fringed paper twisted about the knuckle, and plenty of fresh parsley around the dish. This will always insure an inviting appearance.
Roast Pig.—The modern way of serving a pig is not to send it to the table whole, but have it carved partially by the cook; first, by dividing the shoulder from the body; then the leg in the same manner; also separating the ribs into convenient portions. The head may be divided and placed on the same platter. To be served as hot as possible.
A Spare Rib of Pork is carved by cutting slices from the fleshy part, after which the bones should be disjointed and separated.
A leg of pork may be carved in the same manner as a ham.
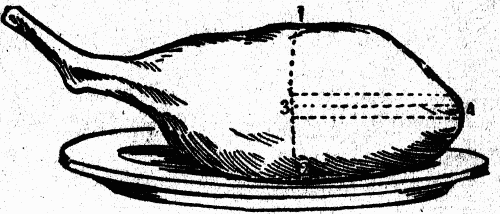
How to Carve Venison
HOW TO CARVE A HAUNCH OF VENISON
A haunch of venison is the prime joint, and is carved very similar to almost any roasted or boiled leg; it should be first cut crosswise down to the bone following the line from 1 to 2; then turn the platter with the knuckle farthest from you, put in the point of the knife, and cut down as far as you can, in the directions shown by the dotted lines from 3 to 4; then there can be taken out as many slices as is required on the right and left of this. Slices of venison should be cut thin, and gravy given with them, but as there is a special sauce made with red wine and currant jelly to accompany this meat, do not serve gravy before asking the guest if he pleases to have any.The fat of this meat is like mutton, apt to cool soon, and become hard and disagreeable to the palate; it should, therefore, be served always on warm plates, and the platter kept over a hot-water dish, or spirit lamp. Many cooks dish it up with a white paper frill pinned around the knuckle bone.
A haunch of mutton is carved the same as a haunch of venison.
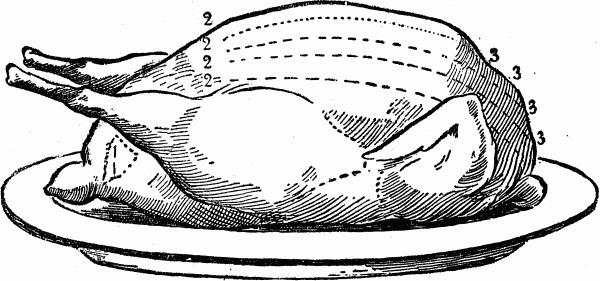
HOW TO CARVE A TURKEY
A turkey having been relieved from strings and skewers used in trussing should be placed on the table with the head or neck at the carver's right hand. An expert carver places the fork in the turkey, and does not remove it until the whole is divided. First insert the fork firmly in the lower part of the breast, just forward of fig. 2, then sever the legs and wings on both sides, if the whole is to be carved, cutting neatly through the joint next to the body, letting these parts lie on the platter.Next, cut downward from the breast from 2 to 3, as many even slices of the white meat as may be desired, placing the pieces neatly on one side of the platter. Now unjoint the legs and wings at the middle joint, which can be done very skillfully by a little practice. Make an opening into the cavity of the turkey for dipping out the inside dressing, by cutting a piece from the rear part 1, 1, called the apron.
Consult the tastes of the guests as to which part is preferred; if no choice is expressed, serve a portion of both light and dark meat. One of the most delicate parts of the turkey are two little muscles, lying in small dish-like cavities on each side of the back, a little behind the leg attachments; the next most delicate meat fills the cavities in the neck bone, and next to this, that on the second joints. The lower part of the leg (or drumstick, as it is called) being hard, tough and stringy, is rarely ever helped to any one, but allowed to remain on the dish.
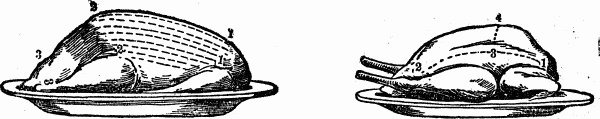
HOW TO CARVE A ROAST GOOSE
To carve a goose, first begin by separating the leg from the body, by putting the fork into the small end of the limb, pressing it closely to the body, then passing the knife under at 2, and turning the leg back as you cut through the joint.To take off the wing, insert the fork in the small end of the pinion, and press it close to the body; put the knife in at fig. 1, and divide the joint. When the legs and wings are off, the breast may be carved in long, even slices, as represented in the lines from 1 to 2.
The back and lower side bones, as well as the two lower side bones by the wing, may be cut off; but the best pieces of the goose are the breast and thighs, after being separated from the drumsticks. Serve a little of the dressing from the inside, by making a circular slice in the apron at fig. 3.
A goose should never be over a year old; a tough goose is very difficult to carve, and certainly most difficult to eat.
HOW TO CARVE A ROAST CHICKEN
First insert the knife between the leg and the body, and cut to the bone; then turn the leg back with the fork, and if the fowl is tender the joint will give away easily. The wing is broken off the same way, only dividing the joint with the knife, in the direction from 1 to 2. The four quarters having been removed in this way, take off the merry-thought and the neck-bones; these last are to be removed by putting the knife in at figs. 3 and 4, pressing it hard, when they will break off from the part that sticks to the breast.To separate the breast from the body of the fowl, cut through the tender ribs close to the breast, quite down to the tail. Now turn the fowl over, back upwards; put the knife into the bone midway between the neck and the rump, and on raising the lower end it will separate readily.
Now turn the rump from you, and take off very neatly the two side bones, and the fowl is carved. In separating the thigh from the drumstick, the knife must be inserted exactly at the joint, for if not accurately hit, some difficulty will be experienced to get them apart; this is easily acquired by practice.
There is no difference in carving roast and boiled fowls if full grown; but in very young fowls the breast is usually served whole; the wings and breast are considered the best parts, but in young ones the legs are the most juicy.
In the case of a capon or large fowl, slices may be cut off at the breast, the same as carving a pheasant.
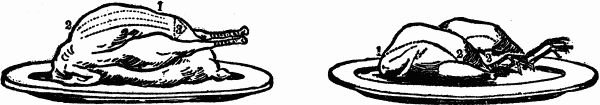
HOW TO CARVE A ROAST DUCK
A young duckling may be carved in the same manner as a fowl, the legs and wings being taken off first on either side. When the duck is full size, carve it like a goose; first cutting it in slices from the breast, beginning close to the wing and proceeding upward towards the breast bone, as is represented by the lines 1 to 2. An opening may be made by cutting out a circular slice, as shown by the dotted lines at number 3.Some are fond of the feet, and when dressing the duck, these should be neatly skinned and never removed. Wild duck is highly esteemed by epicures; it is trussed like a tame duck, and carved in the same manner, the breast being the choicest part.
HOW TO CARVE A ROAST PARTRIDGE
Partridges are generally cleaned and trussed the same way as a pheasant, but the custom of cooking them with the heads on is going into disuse somewhat. The usual way of carving them is similar to a pigeon, dividing it into two equal parts.Another method of carving a roast partridge is to cut it into three pieces, by severing a wing and leg on either side from the body, by following the lines 1 to 2, thus making two servings of those parts, leaving the breast for a third plate.
The third method of carving a roast partridge is to thrust back the body from the legs, and cut through the middle of the breast, thus making four portions that may be served. Grouse and prairie-chicken are carved from the breast when they are large, and quartered or halved when of medium size.

HOW TO CARVE A PHEASANT
Place your fork firmly in the center of the breast of this large game bird and cut deep slices to the bone at figs. 1 and 2; then take off the leg in the line from 3 and 4, and the wing 3 and 5, severing both sides the same. In taking off the wings, be careful not to cut too near the neck; if you do you will hit upon the neck-bone, from which the wing must be separated.
Pass the knife through the line 6, towards the neck, which will detach it. Cut the other parts as in a fowl.
The breast, wings and merry-thought of a pheasant are the most highly prized, although the legs are considered very finely flavored. Pheasants are frequently roasted with the head left on; in that case, when dressing them, bring the head round under the wing, and fix it on the point of a skewer.
HOW TO CARVE PIGEONS
A very good way of carving these birds is to insert the knife at fig. 1, and cut both ways to 2 and 3, when each portion may be divided into two pieces, then served. Pigeons, if not too large, may be cut in halves, either across or down the middle, cutting them into two equal parts; if young and small they may be served entirely whole.
Tame pigeons should be cooked as soon as possible after they are killed, as they very quickly lose their flavor. Wild pigeons, on the contrary, should hang a day or two in a cool place before they are dressed. Oranges cut into halves are used as a garnish for dishes of small birds, such as pigeons, quail, woodcock, squabs, snipe, etc. These small birds are either served whole or split down the back, making two servings.
Other Meat Resources
Now that you know your different meat cuts, do you know how to manage your meat and how to freeze it? See our section on preserving meat for more information on storing, freezing and thawing meat.See our page on Home Butchering with images.
See our page on Deer Hunting Season.
Chart of Beef Cuts of Meat Made Easy.
You can Add your Own Comments on Cuts of Meat and Carving!
We have lots of pages where you can contribute to throughout this website. We love hearing from our readers, and hope you will be one of those we hear from too. Feel free to add anything you like related to cuts of meat and carving.Leave a Comment
Do you have anything that you would like to add after reading this page? We would love to hear your thoughts. If you can add additional information to what has been written here you will be adding value to the website! No need to have any special skills - just type and submit. We will do the rest!







New! Comments
Do you have something of value to add? Leave me a comment in the box below.